Topic
- Around India with MoneyTap 1
- Consumer Durable 1
- Credit Cards 32
- Credit Score 27
- Finance 33
- General 52
- Know MoneyTap Better 26
- MoneyTap 50
- MoneyTap in Daily Life 38
- Personal Loan 86
- Shopping on EMI 4
- Wedding Loan 1
Your credit report not only contains your credit score, but it also has information about your credit activity, payment history and the status of your credit accounts as reported by your lenders and creditors. If you have recently pulled up your credit report and are overwhelmed with so much information, this guide is a good reference point to understand the important aspects of a credit report and learn how to read CIBIL report.
Your credit report contains 6 sections: Credit score, personal information, contact information, employment information, account information, enquiry information
Let’s take a look at each of these sections closely:
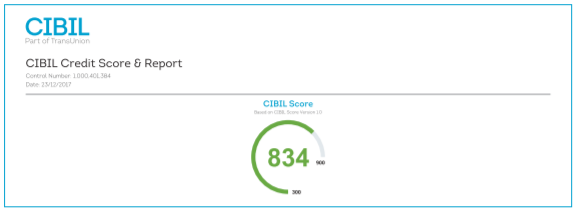
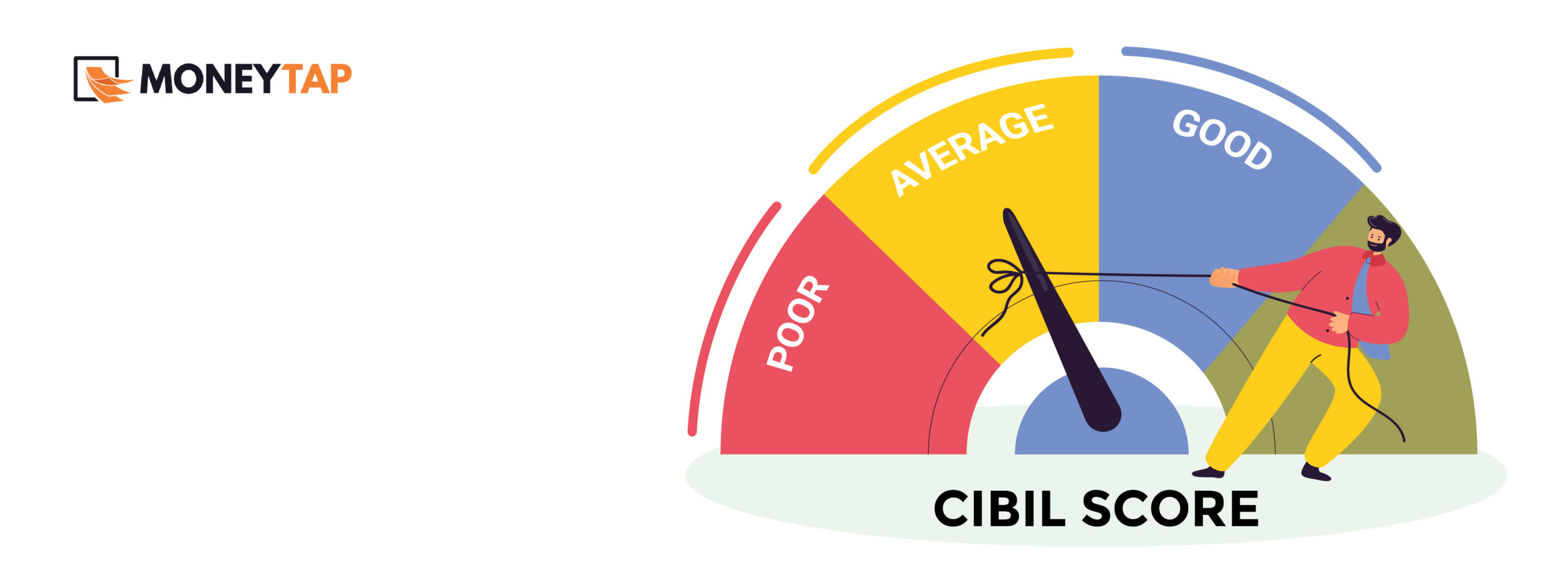
1. Credit Score
Simply put, your credit score reflects your credit health and creditworthiness. It ranges from 300 – 900. The closer your score is to 900, the better is your credit score.
A credit score is one of the key factors in the loan eligibility process. A score of 750 and above is considered ideal for getting loan approvals.
If instead of a 3-digit score, there is ‘NA’ or ‘NH’ on your credit report, it indicates that you don’t have enough credit history or no credit history to get a score. It could also mean that you haven’t had any credit activities for past few years.
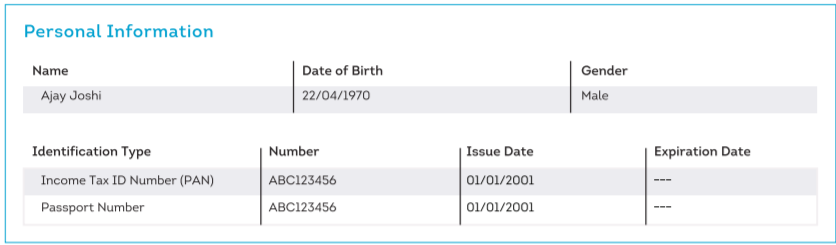
2. Personal Information
This section contains your personal information such as your date of birth, name, PAN Card, as reported by the bank or lender.
Go through the personal details closely and ensure that the details mentioned are accurate.
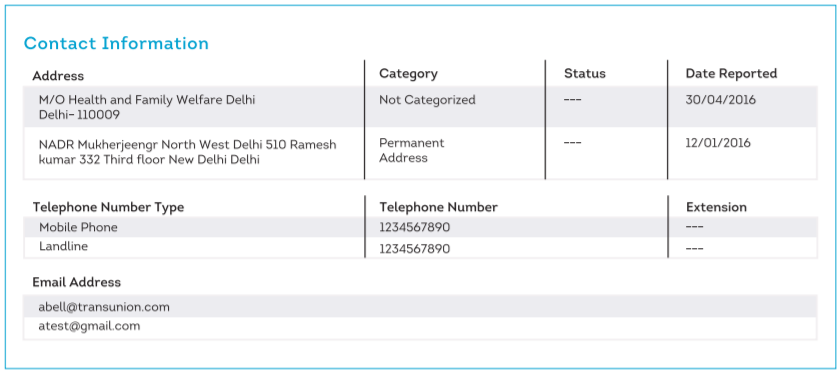
3. Contact Information
The contact details mentioned in this section are as reported by your lender. The section accommodates up to 4 different addresses and email addresses.
The address category segregates the various addresses into a permanent address, residential address and official address.
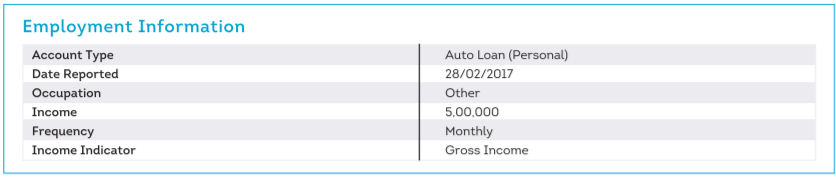
4. Employment Information
This section of the CIBIL report covers your occupation, and monthly and annual income details as reported by the lenders at the time of loan application.
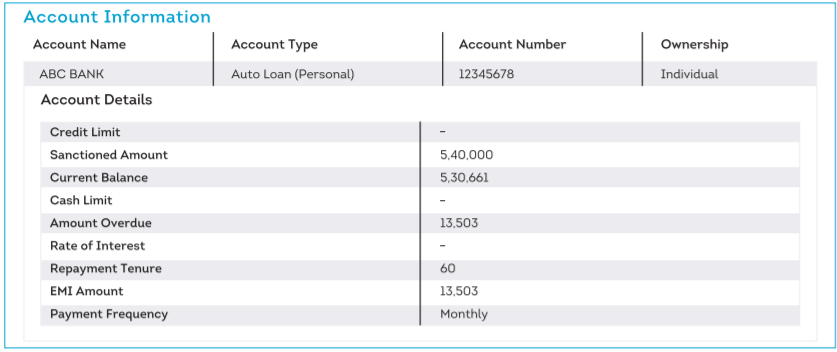
5. Account Information
This section is a very important section as it is about your loan and credit card details. It gives you credit-related information for the last 36 months with details such as the lender’s name, loan amount, type of loan/credit taken, type of loan application (single or joint), date of last payment, outstanding and current balance.
If there is a red-outlined box in the section above the account information, it implies that the information in this section has been disputed. Once the dispute is resolved, the box will disappear. If the dispute has been resolved in your favour, there would be a change in the account information; otherwise, the information will remain the same.
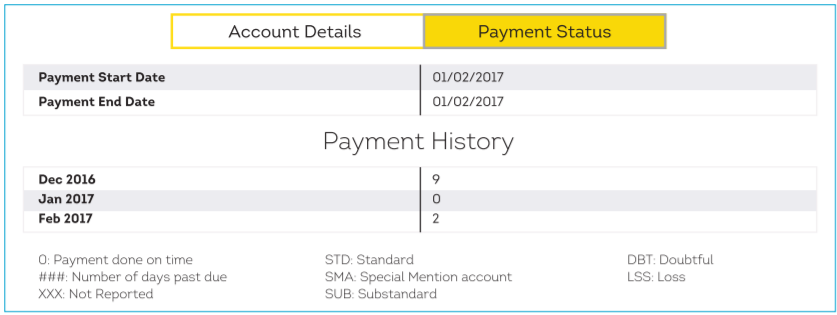
The below section represents your payment behaviour. If there is any irregularity in payments, it will be recorded here.
Payment Status Terms Used In the Credit Report
| STD | Standard | Payments are made within 90 days |
| SUB | Sub-Standard | Payments are made after 90 days |
| SMA | Special Mention Account | Special account created for reporting standard account, moving towards Sub-Standard |
| LSS | Loss | Loss has been identified in the account and it remains uncollectible |
| DBT | Doubtful | The account has been in a Sub-Standard state for 12 months |
Note: If you notice “XXX” reported for your payment details on a certain account, it means that the banks or lenders have not reported the information for those months.
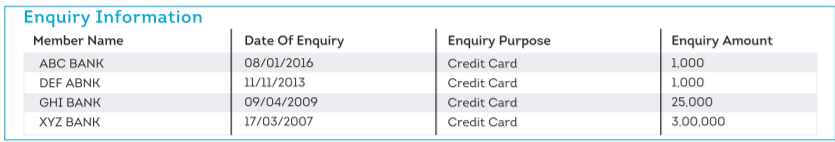
6. Enquiry Information
This section reports the number of enquiries your lenders have made in response to your various credit/loan applications. The details include the lender’s name, type of loan applied for, size of the loan, and date of application.
* Screenshots taken from here.
It’s important that you check your credit report regularly to watch out for possible fraud and identity theft. Knowing how to read CIBIL report can help you keep track of your repayment behaviour, look out for discrepancies and rectify them and understand what steps you should take to improve your credit score.








 Get it on playstore
Get it on playstore Get it on appstore
Get it on appstore